A graphene-based wireless patch that can detect glucose in sweat has been developed by researchers in Korea and the US. The device can also deliver metformin – a drug used to treat diabetes - through the skin to reduce high blood glucose levels in diabetic mice.
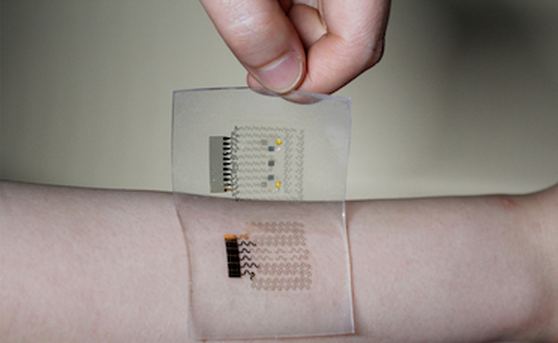 The diabetes patch
The diabetes patchMost commercial glucose sensors available today work by detecting glucose levels in blood, which means that the patient has to go through the painful ordeal of pricking their finger several times a day and dabbing the sensor with blood. The new wearable device, developed by Dae-Hyeong Kim and colleagues at the Institute of Basic Sciences and Seoul National University is non-invasive and is made from a graphene-based electrochemical platform that can monitor blood sugar in a patient’s sweat in real time. The patch can also deliver drugs through microneedles when it detects glucose levels above a certain threshold.
Graphene, a sheet of carbon just one atom thick, shows much promise for use in wearable electronics since it is flexible, soft, conducts electricity very well, and can be transparent. Kim and co-workers added gold particles to graphene and combined it with a gold mesh to produce a flexible, semi-transparent patch that contains a variety of sensors that can detect humidity, glucose, pH and temperature. The device is connected to a portable/wireless power supply and data is sent via a special transmission unit, explains Kim. "It retains its original sensitivity after multiple uses, thereby allowing for multiple treatments."
Painless microneedles
The sensor works using enzymes that are affected by pH in sweat, so the pH and temperature sensors in the device correct the glucose measurements by taking into account these parameters in real time - something that makes it much more reliable. When the patch detects high levels of glucose, heaters embedded in it dissolve the tridecanoic acid polymeric coating on the microneedles in the device so that they can deliver an appropriate amount of medication, such as metformin, as they are inserted (painlessly) into the skin.
The polymer coating also protects the needles from moisture and prevents the metformin from being released too early. The amount of medication delivered in this way can be adjusted by simply varying the number of microneedles.
Device tested on diabetic mice
Experiments on diabetic mice by the researchers show that the blood glucose in the animals decreases significantly over the course of several hours after drug delivery.
"We hope that our patch could be used for non-invasive blood glucose monitoring, so that diabetic patients can avoid painful blood-drawing and insulin shots," says team member Hyunjae Lee.
Richard Guy of the University of Bath in the UK says that "some important questions still need to be answered before the technology can be translated into practical use." For example, can the sensor function over time periods as long as 24 hours? Will the device still be reliable if the wearer is sweating a lot? How frequently will the sensor be calibrated; and how sensitive is the device to hypoglycaemia – which is a particular worry in young diabetics?
"It is probably safe to say that these issues are already being addressed and that other therapeutic strategies are being identified to complement the significant advances achieved in this work," he writes. "Thus, although the holy grail of diabetes management - a non-invasive feedback system combining glucose monitoring and responsive drug delivery - is not yet at hand, Kim and co-workers have certainly moved the field closer to this coveted prize."

